In recent years, 3D printing has become a game-changer in the world of architecture, offering architects a revolutionary way to create highly detailed and accurate building models. This cutting-edge technology enables architects to quickly produce prototypes, enhance their designs, and even print full-scale building components, all while reducing costs and material waste. In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into the top 3D printing tools for architecture and how they are transforming the design and construction processes.
1. How 3D Printing Works in Architecture
3D printing in architecture works by translating digital designs created using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software into physical, three-dimensional objects. By layering materials such as plastic, concrete, and metals, 3D printers can build complex architectural models with unmatched precision. This process allows architects to visualize their designs in real-world form before starting actual construction.
2. Top 3D Printing Tools Revolutionizing Architectural Models
1. Stratasys Fortus 450mc
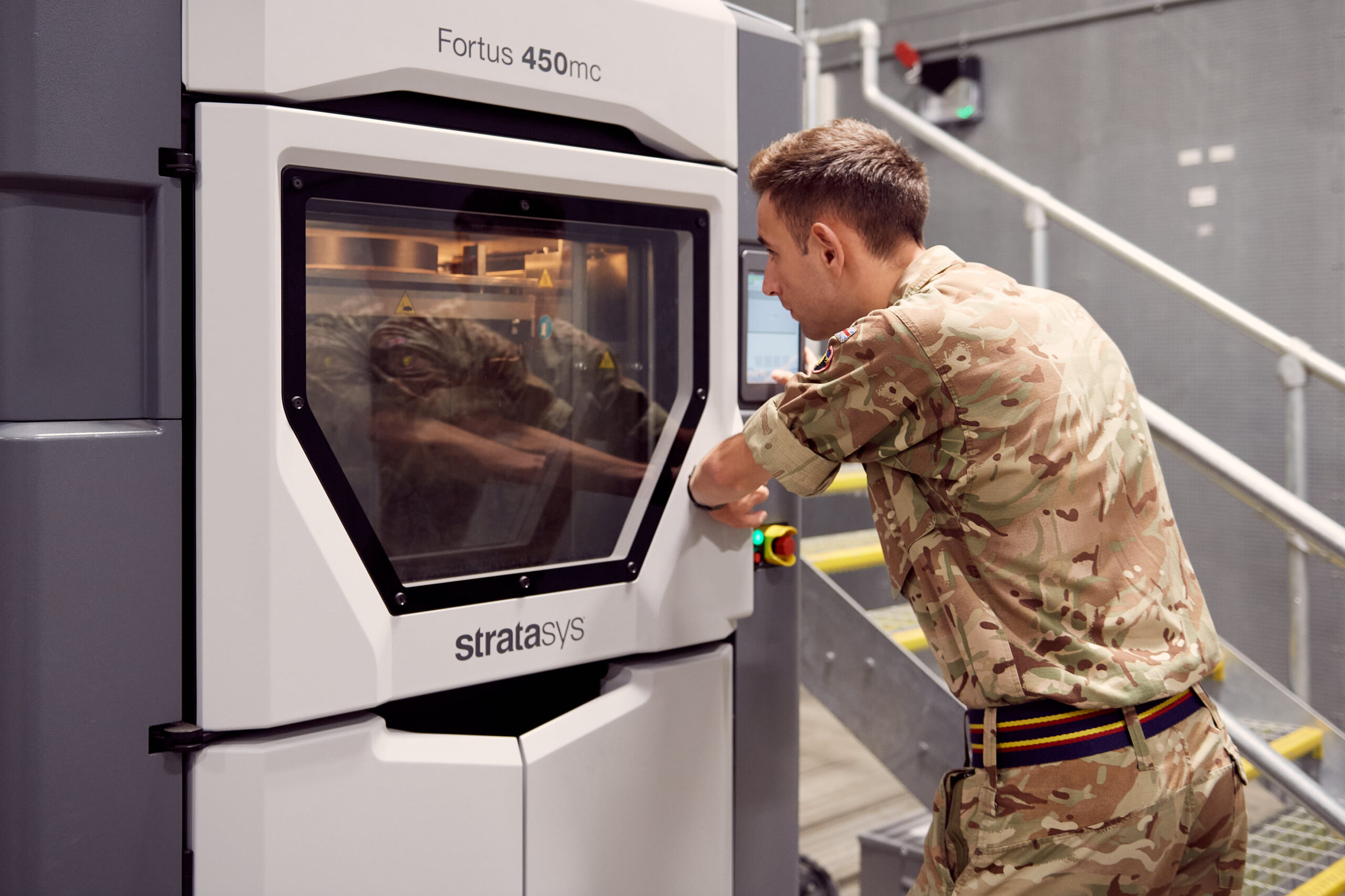

- Overview: The Stratasys Fortus 450mc is an industry-leading 3D printer widely used in architecture for producing durable and high-precision models. It’s particularly useful for creating structural prototypes that require high strength and accuracy.
- Key Features: Fast printing speed, a wide range of thermoplastic materials, and the ability to create complex, intricate designs that are often required in architectural projects.
2. Formlabs Form 3
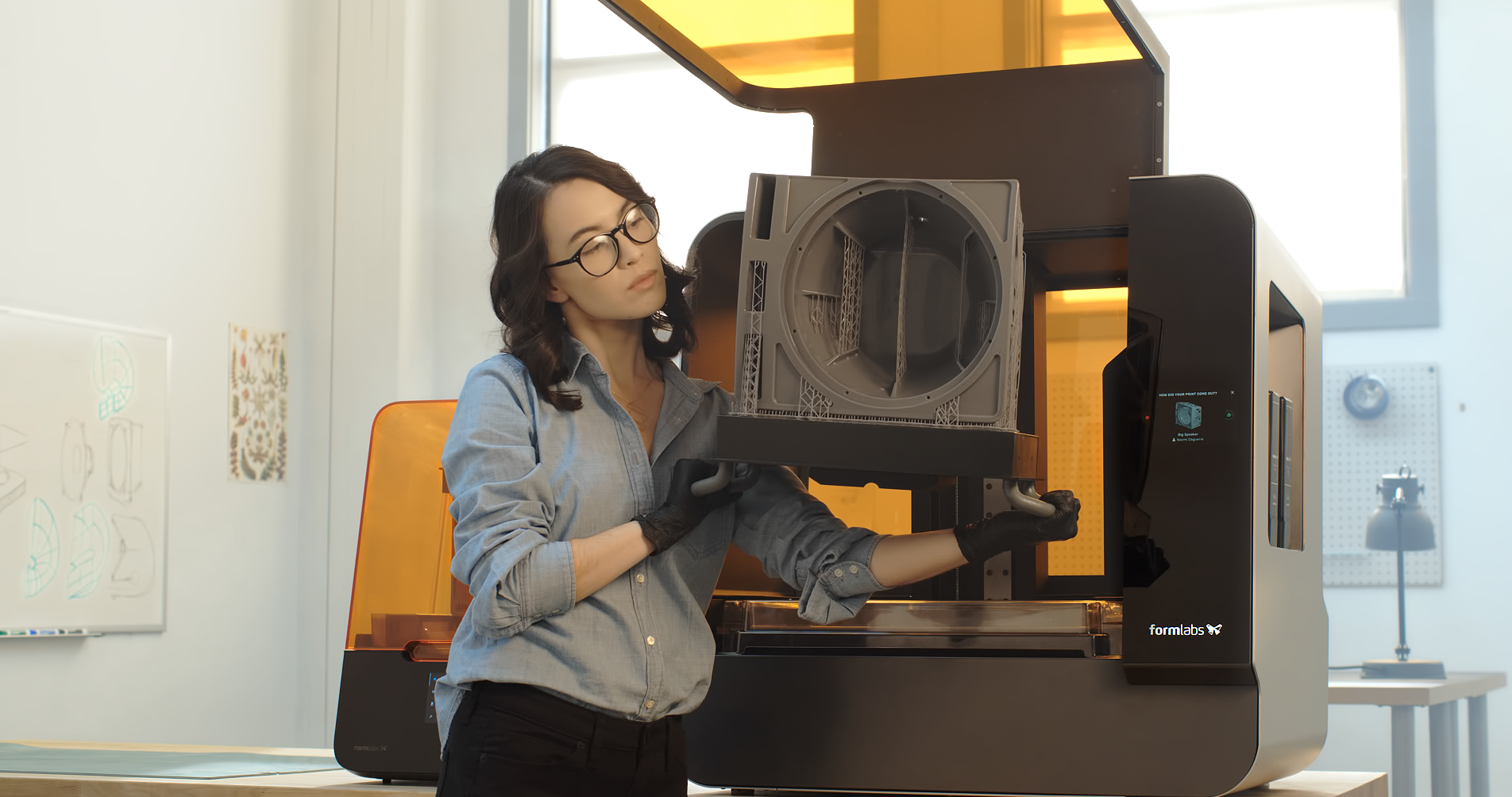

- Overview: The Formlabs Form 3 is known for its ability to print incredibly detailed architectural models using resin-based materials. It’s perfect for creating architectural miniatures or detailed design elements.
- Key Features: High resolution, versatile resin materials, and excellent precision, making it ideal for fine details and small-scale architectural models.
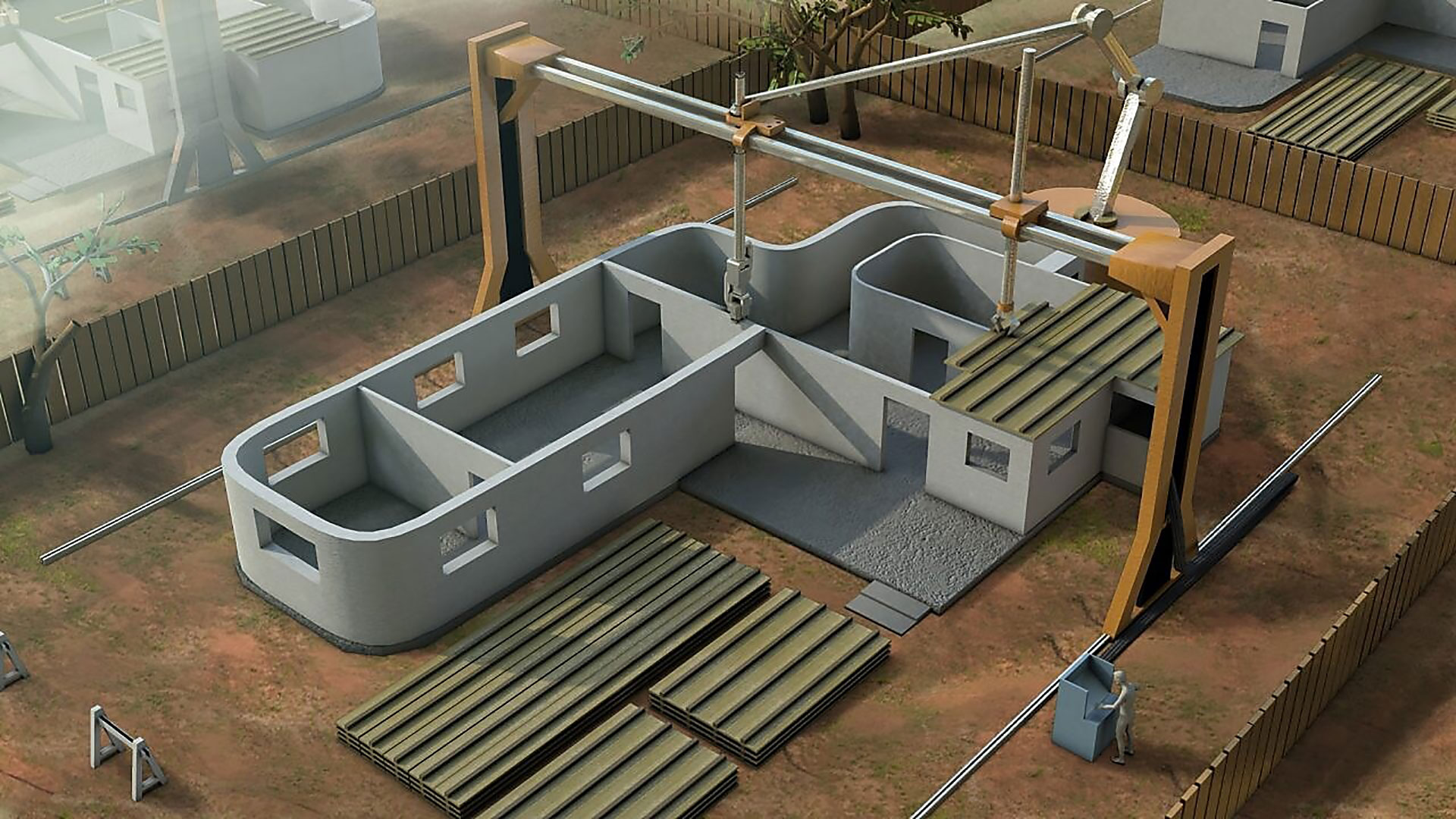
3. WASP 3D Printers (Concrete Printing)

- Overview: WASP 3D printers specialize in 3D printing with concrete, allowing architects to print full-scale buildings or structural components. This innovation is changing the way large-scale construction projects are carried out.
- Key Features: Large-format 3D printing capabilities, sustainability-focused designs, and the ability to print eco-friendly buildings or architectural features.
4. LulzBot TAZ 6

- Overview: LulzBot TAZ 6 is an affordable yet powerful 3D printer that’s well-suited for architects who want to experiment with various materials to bring their designs to life.
- Key Features: Compatibility with a wide range of materials (including plastics and metals), easy-to-use interface, and reliable, high-quality prints ideal for architectural prototypes.
3. Materials for 3D Printing in Architecture
- Plastics (ABS, PLA):
Plastics like ABS and PLA are the most commonly used materials for 3D printing architectural models. They are lightweight, easy to handle, and ideal for creating smaller models or design elements. As a result, they are perfect for detailed prototypes and quick mock-ups. - Concrete:
On the other hand, concrete is becoming increasingly popular in the architecture industry, especially for printing full-scale structures and building components. It is strong, durable, and allows for fast prototyping of larger architectural designs. This material is particularly useful when working on bigger projects, like walls or foundations.

- Metals (Stainless Steel, Titanium): Some advanced 3D printers allow architects to print with metals, offering structural integrity and the possibility to create complex, functional building elements such as custom fixtures or exterior details.
- Resins: Resin printing is ideal for producing highly detailed and precise architectural models, particularly for client presentations or as physical representations of intricate designs.
4. The Benefits of 3D Printing in Architecture
- Speed and Efficiency: 3D printing allows architects to accelerate the prototyping process, turning digital designs into physical models in a fraction of the time required by traditional methods.
- Customization: With 3D printing, architects can easily customize designs and adapt them to client needs, creating unique, tailor-made building models.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to traditional model-making methods, 3D printing significantly reduces material waste and labor costs, allowing for more affordable design prototypes.
- Sustainability: 3D printing promotes sustainability in architecture by using eco-friendly materials and reducing the waste generated during the construction process.
5. Real-World Applications of 3D Printing in Architecture
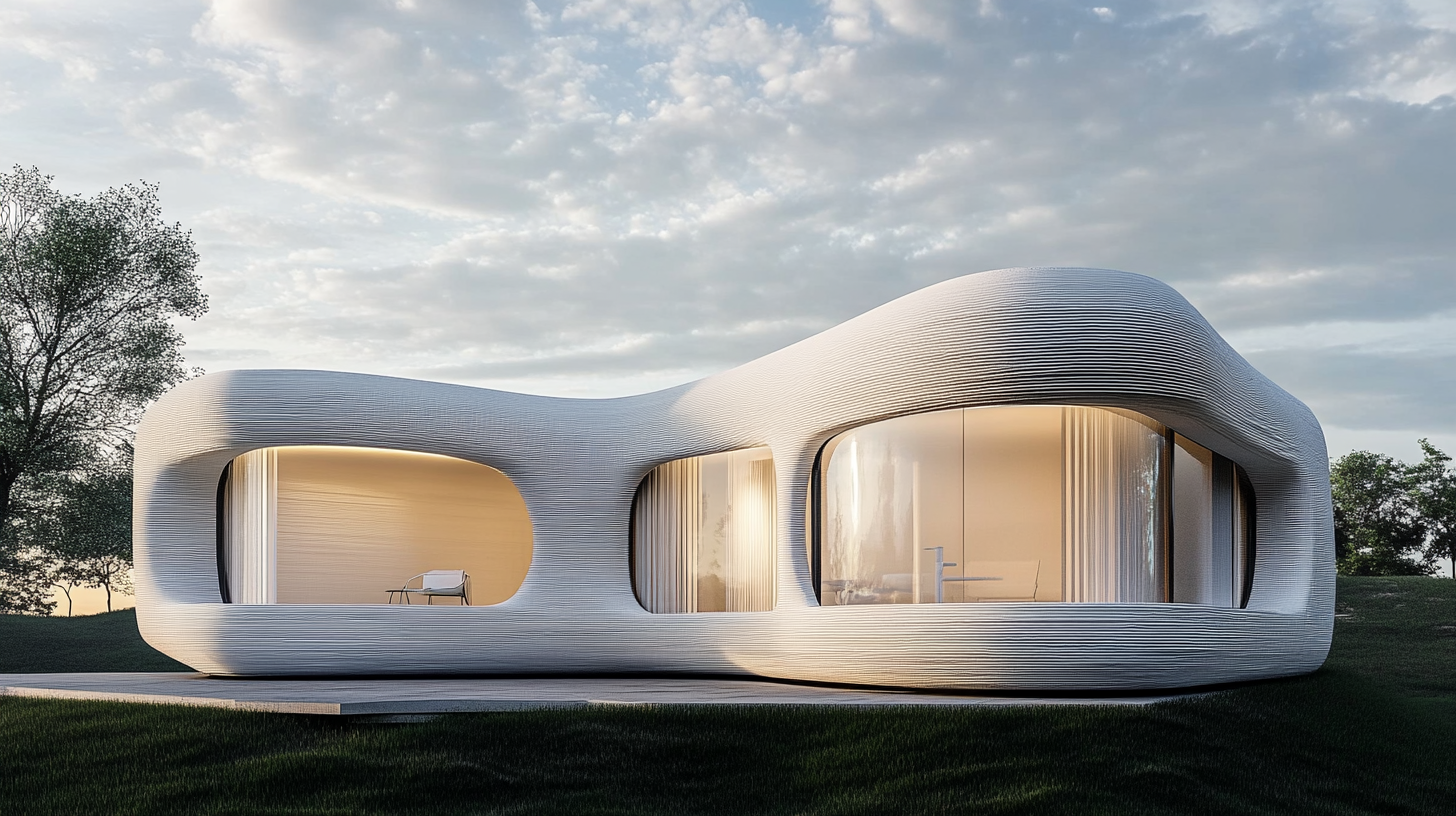

- Prototyping and Model Making: 3D printing in architecture is primarily used for creating accurate and detailed prototypes, giving clients a tangible representation of what the final design will look like before construction begins.
- Full-Scale Building Projects: Leading-edge projects, such as 3D-printed homes and structures, are demonstrating how this technology can be used to print entire buildings, offering faster and more affordable construction methods.
- Historic Building Preservation: 3D printing is also being used in the restoration of historic buildings by recreating missing or damaged architectural details with precision, preserving cultural heritage for future generations.
6. The Challenges and Future of 3D Printing in Architecture
- Challenges: While 3D printing offers tremendous potential, there are still challenges to overcome, such as limitations in material diversity, the size of printable objects, and building regulations that must adapt to new technologies.
- The Future: The future of 3D printing in architecture is incredibly promising, with potential applications ranging from 3D-printed cities to eco-friendly and self-sustaining structures. As the technology advances, it will continue to shape the future of building design and construction.
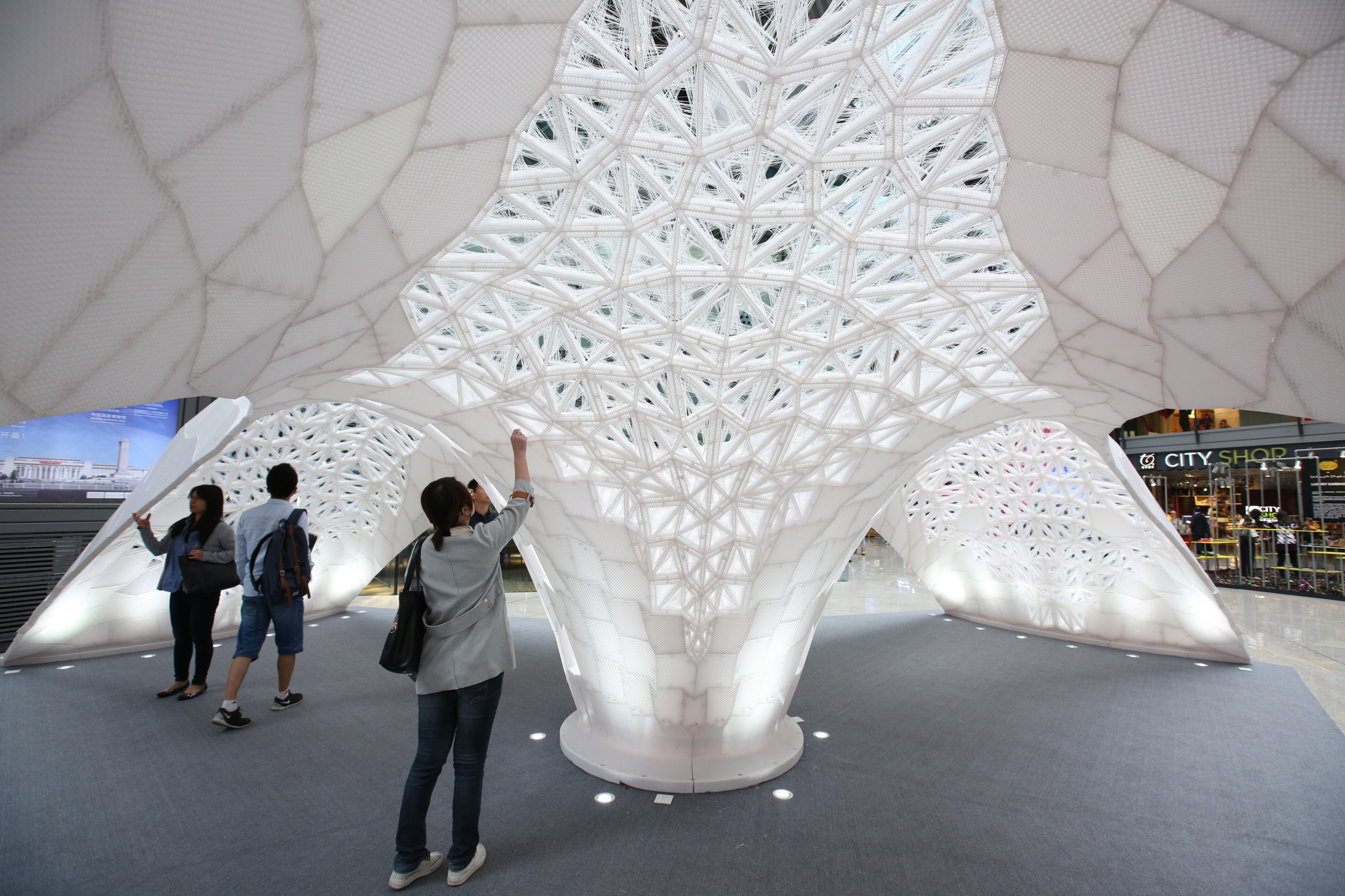

Embracing the Power of 3D Printing in Architecture
3D printing is a revolutionary tool in the world of architecture, offering architects new possibilities for creativity, efficiency, and sustainability. Whether it’s creating intricate models, prototyping large-scale structures, or even constructing buildings, 3D printing is paving the way for a more innovative and sustainable future in architectural design.